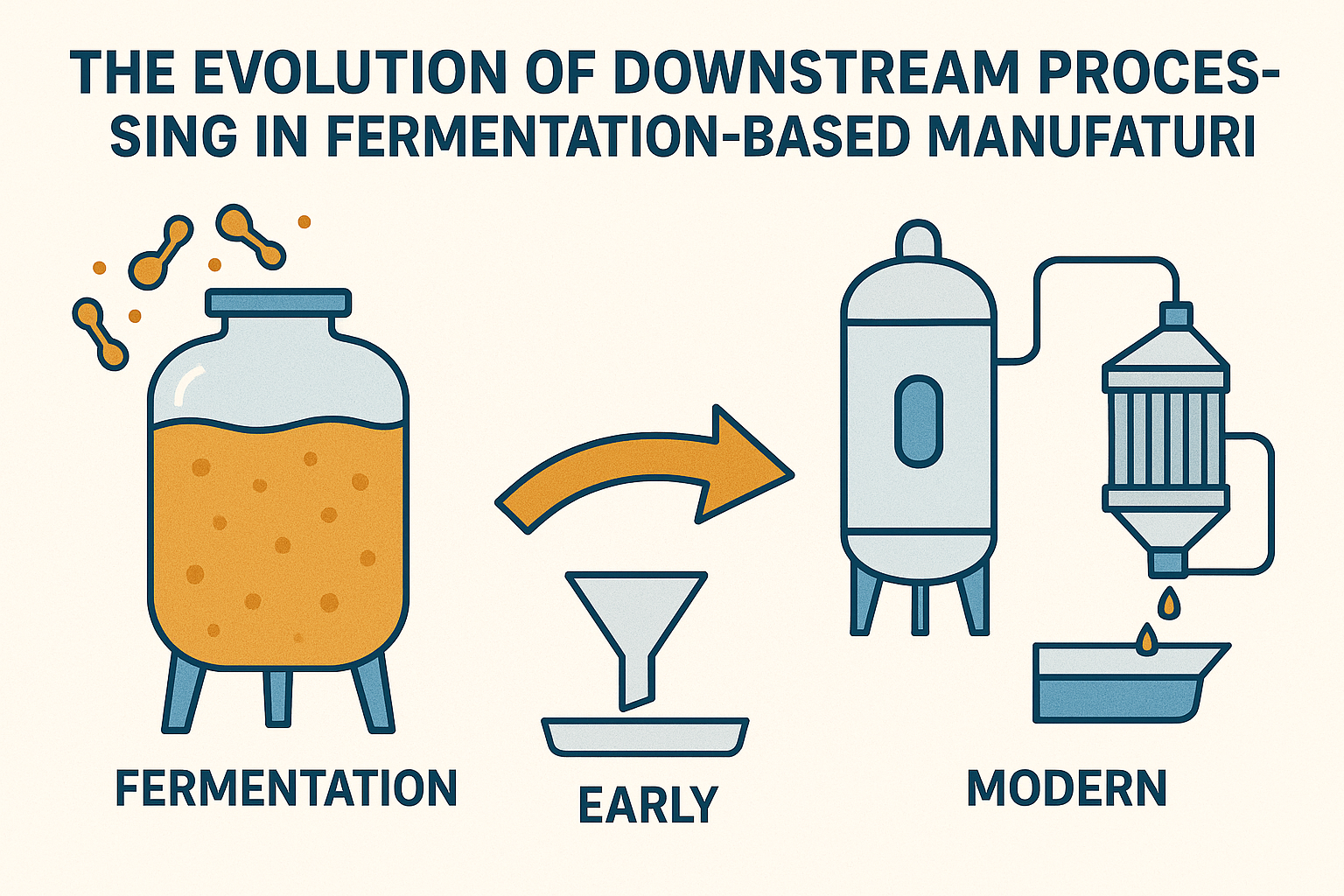
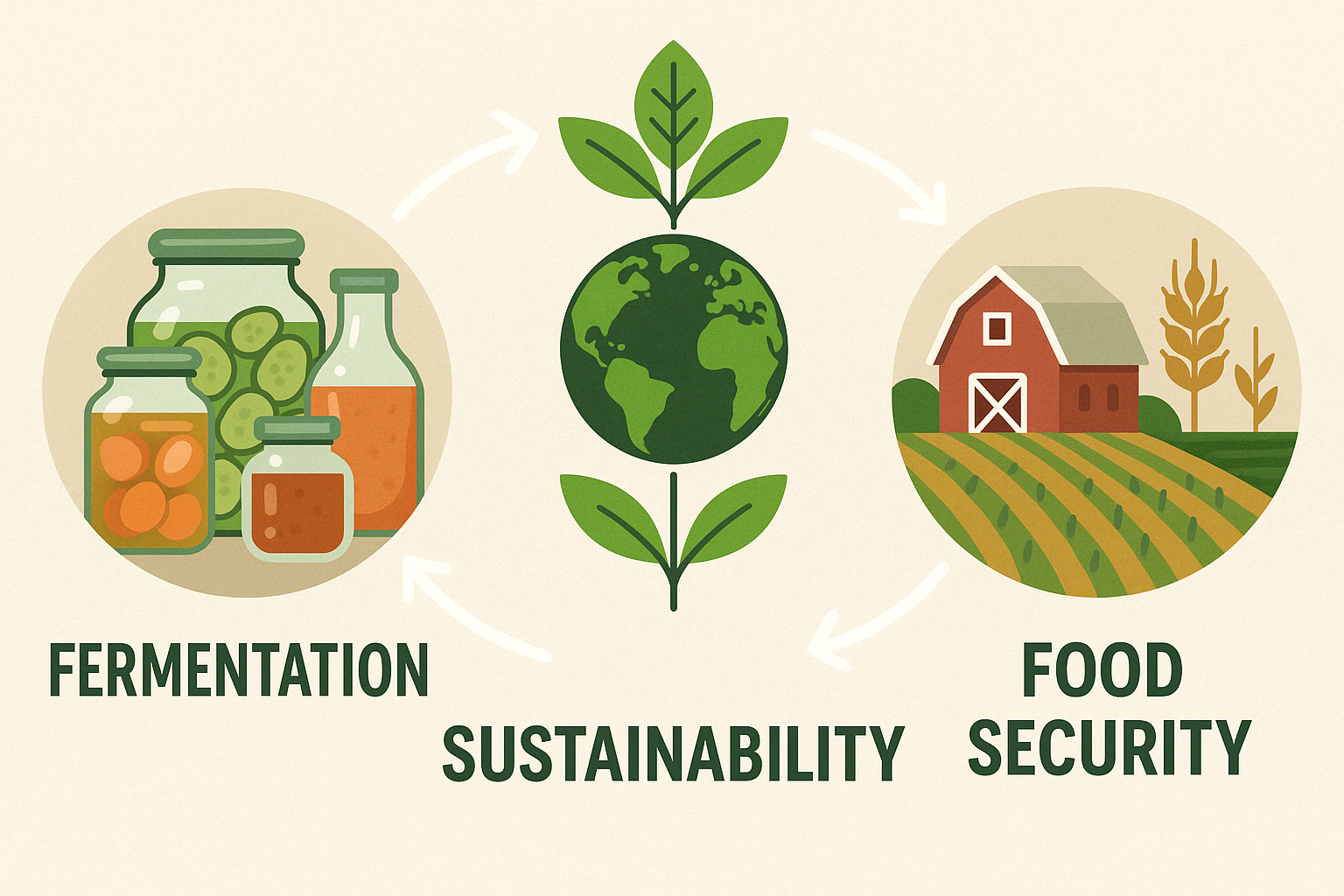
The challenge of producing enough food to feed a growing global population while minimizing environmental impact is one of the most pressing issues of our time. Traditional agriculture, especially livestock farming, places enormous strain on natural resources, contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, and leads to deforestation and loss of biodiversity. As concerns over climate change and sustainability intensify, the Agri-Foodtech industry is turning to innovative technologies such as fermentation to provide alternative solutions.
The Basics of Fermentation in Food Production
Fermentation is a natural metabolic process through which microorganisms such as bacteria, yeast, and fungi convert organic substances into simpler compounds. This process has been utilized by humans for centuries to produce foods like bread, beer, yogurt, and cheese. Today, fermentation is being harnessed in new and advanced ways to create proteins, enzymes, bioactive compounds, and other functional ingredients that are essential for sustainable food production.
Fermentation’s Contribution to Sustainability
One of the primary reasons fermentation is gaining popularity as a sustainable food production method is its efficiency. Unlike traditional livestock farming, fermentation-based protein production requires significantly less land, water, and energy. Microorganisms can be cultivated in controlled environments that are not dependent on climate or geographical conditions, allowing for year-round production with consistent quality.
Additionally, fermentation processes can be highly targeted and optimized for specific outcomes. Through precision fermentation and metabolic engineering, scientists can design microorganisms to produce proteins, lipids, and other valuable compounds with minimal waste. This approach not only reduces resource consumption but also decreases the carbon footprint associated with food production.
Replacing Animal-Based Products with Fermentation-Derived Alternatives
A major area where fermentation is making an impact on sustainability is in the development of alternative proteins. Fermentation-derived proteins can be used to create plant-based meats, dairy-free cheeses, and other animal-free food products that closely mimic the taste, texture, and nutritional profile of their conventional counterparts.
By reducing reliance on animal agriculture, fermentation helps mitigate the negative environmental impacts associated with livestock farming, such as methane emissions, water pollution, and habitat destruction. Furthermore, fermentation-based foods are free from antibiotics and growth hormones, enhancing food safety and consumer health.
Fermentation for Functional Ingredients and Nutraceuticals
Beyond proteins, fermentation technology is also being applied to produce bioactive compounds and functional ingredients that offer additional health benefits. For example, probiotics, vitamins, and antioxidants can be produced more efficiently through fermentation processes than through conventional extraction or synthesis methods.
The production of these nutraceuticals through fermentation not only reduces the environmental impact associated with chemical synthesis but also provides opportunities for creating novel health-enhancing products that promote well-being.
Circular Economy and Waste Reduction
Fermentation processes can contribute to a circular economy by utilizing agricultural by-products and food waste as substrates for microbial cultivation. By converting waste streams into valuable products, fermentation can help reduce the environmental burden of food production while promoting resource efficiency.
Moreover, the ability to repurpose organic waste into high-value ingredients presents opportunities for companies to enhance their sustainability credentials and differentiate themselves in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While fermentation holds significant promise for sustainable food production, challenges remain. Scaling up fermentation processes to meet global demand requires substantial investment in infrastructure, expertise, and regulatory compliance. Additionally, ensuring cost competitiveness with traditional agricultural methods remains an ongoing concern.
Despite these challenges, continued advancements in biotechnologycell engineering, process optimization, and collaboration across the Agri-Foodtech ecosystem are paving the way for fermentation to play a central role in the future of sustainable food production. Companies like YD LabsYDLabs are at the forefront of this movement, providing the expertise and infrastructure needed to bring fermentation-based solutions to scale.
Conclusion
The role of fermentation in sustainable food production is becoming increasingly apparent as the industry seeks to address critical issues related to climate change, resource efficiency, and food security. By leveraging innovative fermentation technologies, companies can reduce their environmental impact while producing high-quality, nutritious, and safe food products. As research and development efforts continue to advance, fermentation is poised to play an even more significant role in creating a resilient and sustainable global food system.